Lateral Thinking Vs Design Thinking
What's the difference and when to use to use which one
While both lateral thinking and design thinking aim to foster creativity and innovation they differ in their methods and focus areas. Lateral thinking focuses on disrupting traditional thought patterns to generate new ideas, whereas design thinking centers on understanding user needs and creating practical, user-centered solutions through a structured process.
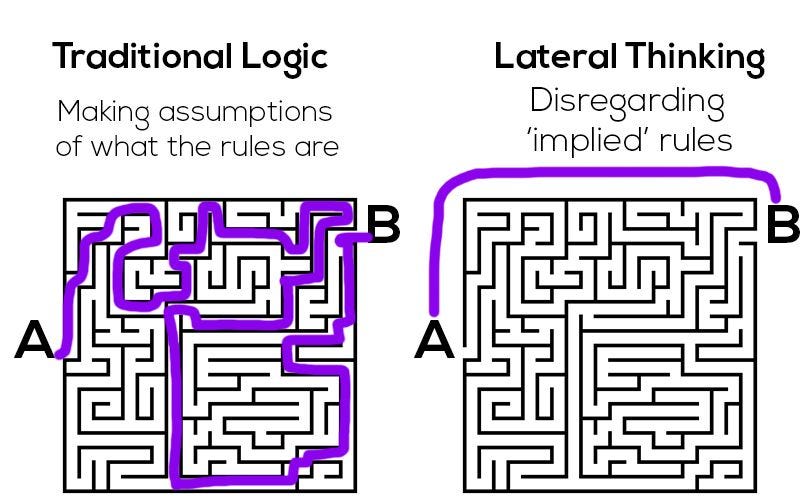
LATERAL THINKING
Focus: Generating new ideas by breaking away from traditional, linear thought processes.
Objective: Aims to disrupt conventional thinking and generate novel ideas.
Applications: Broadly applicable across various domains requiring creative solutions.
Approach:
Provocation: Introducing unexpected, random ideas to disrupt established patterns of thinking.
Challenge: Questioning and challenging existing assumptions and norms.
Alternatives: Exploring multiple, diverse possibilities and approaches.
Analogies and Patterns: Using analogies and patterns to inspire new solutions.
Usage: Can be applied in various fields where innovative and creative thinking is required, such as business strategy, marketing, and problem-solving.
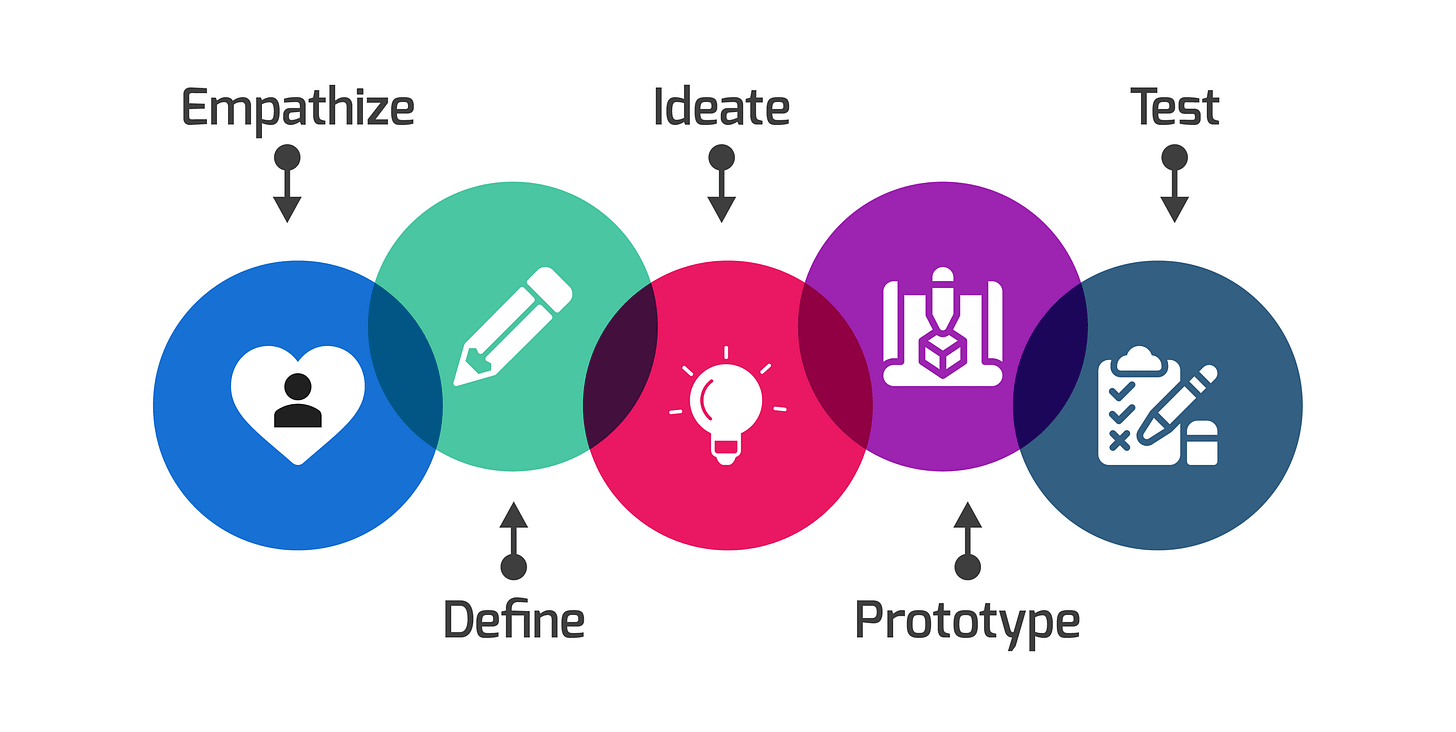
DESIGN THINKING
Focus: Human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving, primarily in design and product development.
Objective: Solving specific problems by understanding and addressing user needs.
Applications: Primarily used in design and development contexts to create user-centered products and services.
Approach:
Empathize: Understanding the needs, experiences, and motivations of end-users.
Define: Clearly articulating the problem based on insights gathered from the empathize phase.
Ideate: Generating a wide range of ideas and solutions through brainstorming sessions.
Prototype: Creating tangible representations of ideas to test and explore their feasibility.
Test: Gathering feedback from users to refine and improve solutions.
Usage: Widely used in product design, user experience (UX) design, and service design, focusing on creating solutions that are both innovative and user-centric.